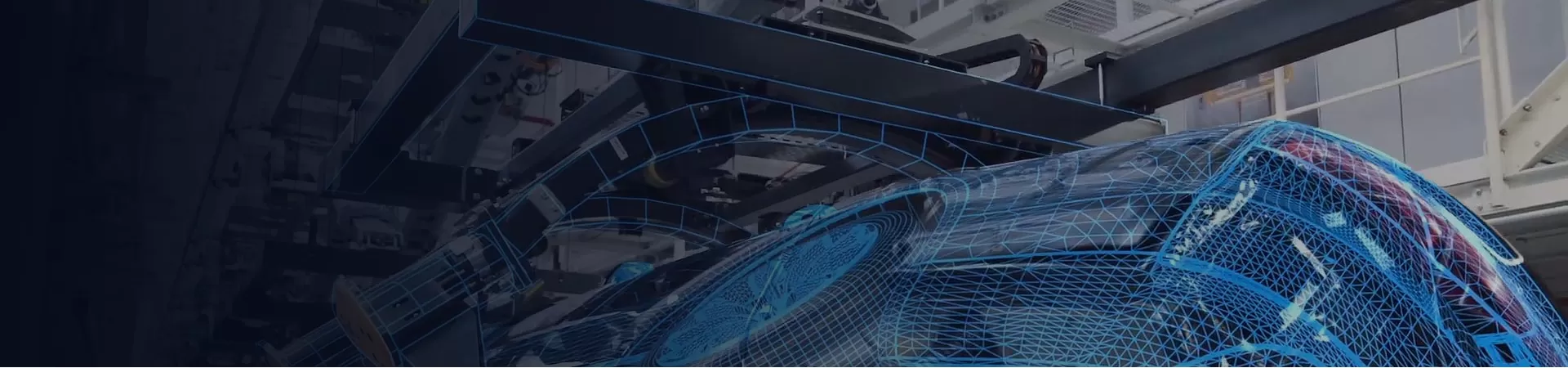
Metal stamping is essential for high-volume, precision manufacturing because it allows for the rapid production of consistent, complex metal parts with tight tolerances at a relatively low cost, making it ideal for applications where large quantities of identical components are needed with high quality standards, particularly in industries like automotive, electronics, and medical devices.

In modern manufacturing, the need for high-precision, high-volume production has never been more critical. From automotive components to electronics and aerospace parts, the demand for quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness drives manufacturers to adopt metal stamping as a preferred method for producing complex and precise components. As a key technique in industries ranging from automotive to consumer electronics, metal stamping offers superior accuracy, reduced costs, and the ability to meet high-volume demands.
This article will explore why metal stamping is a cornerstone of precision manufacturing and why it remains essential in the competitive world of high-volume production.
The Growing Importance of Metal Stamping
Metal stamping is a manufacturing process that shapes metal sheets into specific forms using a die and a stamping press. As the global manufacturing industry continues to evolve, market demand for metal stamping is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3%, reaching $243 billion by 2027 (Grand View Research). The reason behind this steady growth lies in the cost-effectiveness and high precision that stamping offers, particularly for mass production of parts across various sectors, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
Key Benefits of Metal Stamping for High-Volume Production
1. High Precision and Consistency
One of the primary reasons metal stamping is indispensable in precision manufacturing is its ability to achieve high accuracy in producing parts. With tightly controlled tolerances, stamping can create parts with repeatable consistency, which is crucial for industries that demand uniformity in product performance. For example, automotive manufacturers rely on metal stamping to produce metallic body panels, engine components, and safety features with exact specifications.
Precision tolerance range: typically ±0.001 inches for thin metal sheets.
Ideal for parts that require tight tolerances, such as electronic connectors and precision brackets.
The use of advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and progressive stamping dies enhances the precision of metal stamping even further, ensuring that complex parts are produced with minimal defects and maximum accuracy.
2. Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
Metal stamping is one of the most cost-effective manufacturing processes for high-volume production. Once the initial die design and setup are complete, the cost per unit decreases significantly, making it ideal for mass production.
Low cost per part due to automation and reduced labor costs.
Lower material wastage compared to other methods like machining.
Faster production cycles, increasing output and reducing overall manufacturing costs.
In fact, companies that adopt advanced stamping technologies have reported up to 30% cost reduction in their production runs (Deloitte).
3. Versatility in Material Use
Metal stamping allows manufacturers to work with a variety of materials, such as steel (carbon and stainless), aluminum, brass, copper, and even titanium. This versatility makes stamping applicable in a wide range of industries. Whether producing lightweight automotive parts, heavy-duty industrial machinery components, or high-precision electronic devices, metal stamping ensures that the correct material properties are achieved for each application.
Metals commonly used in stamping include steel, aluminum, brass, titanium, and more.
The ability to create both simple and complex parts makes it suitable for industries like aerospace, consumer electronics, and medical devices.
4. Ability to Achieve Complex Geometries
Another significant advantage of metal stamping is its ability to produce complex shapes and intricate designs. Deep-draw stamping and progressive stamping are two common techniques that allow manufacturers to form deep, complex geometries while maintaining tight tolerances.
Deep draw stamping enables the creation of 3D shapes, such as automotive body panels and enclosures for electronic devices.
Progressive dies enable multiple operations in a single pass, reducing production time and handling costs.
This capability to produce complex features such as embossed designs, perforations, and folded edges is crucial for products in aerospace, electronics, and medical equipment.
5. Reliability and Consistency
The automation inherent in metal stamping ensures that each part is produced with the same level of quality and precision, minimizing defects and increasing consistency across high-volume production runs. For industries like medical device manufacturing, where reliability is crucial, metal stamping ensures that every component meets exact specifications.
Fewer defects and rework due to the automated, repeatable nature of stamping.
ISO-certified processes ensure compliance with international quality standards.
Applications of Metal Stamping in Key Industries
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is one of the largest users of metal stamping, with hundreds of parts in each vehicle requiring precise and durable components. These include body panels, brackets, frames, and safety mechanisms. High-volume metal stamping meets the needs of car manufacturers by providing low-cost, high-quality parts that meet rigorous safety standards.
Electronics and Electrical Components
Metal stamping is also critical in the production of connectors, enclosures, battery terminals, and heat sinks for the electronics industry. The need for compact, high-precision parts makes metal stamping essential in the design of smartphones, computers, and telecommunication devices.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace manufacturers require high-strength and lightweight components that meet strict safety and performance regulations. Metal stamping is used to produce aircraft structural parts, fasteners, and engine components with high precision and reliability.
Consumer Goods
From appliance covers to decorative frames and functional parts, metal stamping serves the consumer goods industry by providing cost-effective and durable components for a variety of products.
Conclusion
Metal stamping is not just a manufacturing process—it's an essential technology for high-volume, precision manufacturing. Its ability to produce complex parts with high accuracy at cost-effective rates makes it indispensable for industries like automotive, electronics, aerospace, and consumer goods. As a manufacturer, investing in advanced metal stamping technologies will enhance your production efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the increasing demand for high-quality components. By partnering with an experienced metal stamping supplier, businesses can ensure they receive precise, reliable, and cost-effective solutions to meet the challenges of high-volume manufacturing.
If you are looking for a trusted metal stamping partner, we offer comprehensive services from design to production, delivering high-quality solutions that meet the needs of your industry.